
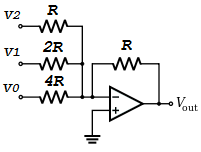
A disadvantage of the former DAC design was its requirement of several different precise input resistor values: one unique value per binary input bit. It is recommended that CMOS output gates are used, and that input/feedback resistor values are chosen so as to minimize the amount of current each gate has to source or sink.Īn alternative to the binary-weighted-input DAC is the so-called R/2R DAC, which uses fewer unique resistor values. Likewise, all "low" voltage levels should be identical between gates, ideally 0.00 volts exactly. If one gate is outputting +5.02 volts for a "high" while another is outputting only +4.86 volts, the analog output of the DAC will be adversely affected. It should be noted that all logic gates must output exactly the same voltages when in the "high" state. If we wish to expand the resolution of this DAC (add more bits to the input), all we need to do is add more input resistors, holding to the same power-of-two sequence of values: For example, by making the feedback resistor 800 Ω instead of 1 kΩ, the DAC will output -1 volt for the binary input 001, -4 volts for the binary input 100, -7 volts for the binary input 111, and so on. We can adjust resistors values in this circuit to obtain output voltages directly corresponding to the binary input. The output voltage appears on node 6 in the simulation: In the following simulation, I set up the DAC circuit with a binary input of 110 (note the first node numbers for resistors R 1, R 2, and R 3: a node number of "1" connects it to the positive side of a 5 volt battery, and a node number of "0" connects it to ground).

This circuit is very easy to simulate using SPICE. Note that with each step in the binary count sequence, there results a 1.25 volt change in the output. If we chart the output voltages for all eight combinations of binary bits (000 through 111) input to this circuit, we will get the following progression of voltages:
DIGITAL TO ANALOG AUDIO CONVERTER CIRCUIT DIAGRAM FULL
If we drive the inputs of this circuit with digital gates so that each input is either 0 volts or full supply voltage, the output voltage will be an analog representation of the binary value of these three bits. These ratios are were not arbitrarily chosen: they are the same ratios corresponding to place weights in the binary numeration system. In other words, input voltage V 1 has a 1:1 effect on the output voltage (gain of 1), while input voltage V 2 has half that much effect on the output (a gain of 1/2), and V 3 half of that (a gain of 1/4).

Starting from V 1 and going through V 3, this would give each input voltage exactly half the effect on the output as the voltage before it. Suppose we were to set the input resistor values at multiple powers of two: R, 2R, and 4R, instead of all the same value R: Let's consider, however, intentionally setting the input resistors at different values. If any of the input resistors were different, the input voltages would have different degrees of effect on the output, and the output voltage would not be a true sum. The output voltage is the inverted (opposite polarity) sum of all input voltages:įor a simple inverting summer circuit, all resistors must be of equal value. If you recall, the classic inverting summer circuit is an operational amplifier using negative feedback for controlled gain, with several voltage inputs and one voltage output.
This DAC circuit, otherwise known as the binary-weighted-input DAC, is a variation on the inverting summer op-amp circuit. Therefore, we will begin with DAC circuitry and then move to ADC circuitry. It is much easier to convert a digital signal into an analog signal than it is to do the reverse. Together, they are often used in digital systems to provide complete interface with analog sensors and output devices for control systems such as those used in automotive engine controls: In block diagram form, it looks like this: In block diagram form, it can be represented as such:Ī DAC, on the other hand, inputs a binary number and outputs an analog voltage or current signal. An analog-to-digital converter, or ADC, performs the former task while a digital-to-analog converter, or DAC, performs the latter.Īn ADC inputs an analog electrical signal such as voltage or current and outputs a binary number. What is needed is a way to electronically translate analog signals into digital (binary) quantities, and visa-versa. However, when analog devices are involved, interfacing becomes much more complex. Switches, relays, and encoders are easily interfaced with gate circuits due to the on/off nature of their signals. Lessons In Electric Circuits - Volume IV Chapter 13Ĭonnecting digital circuitry to sensor devices is simple if the sensor devices are inherently digital themselves. Lessons In Electric Circuits - Volume IV (Digital) - Chapter 13


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
